
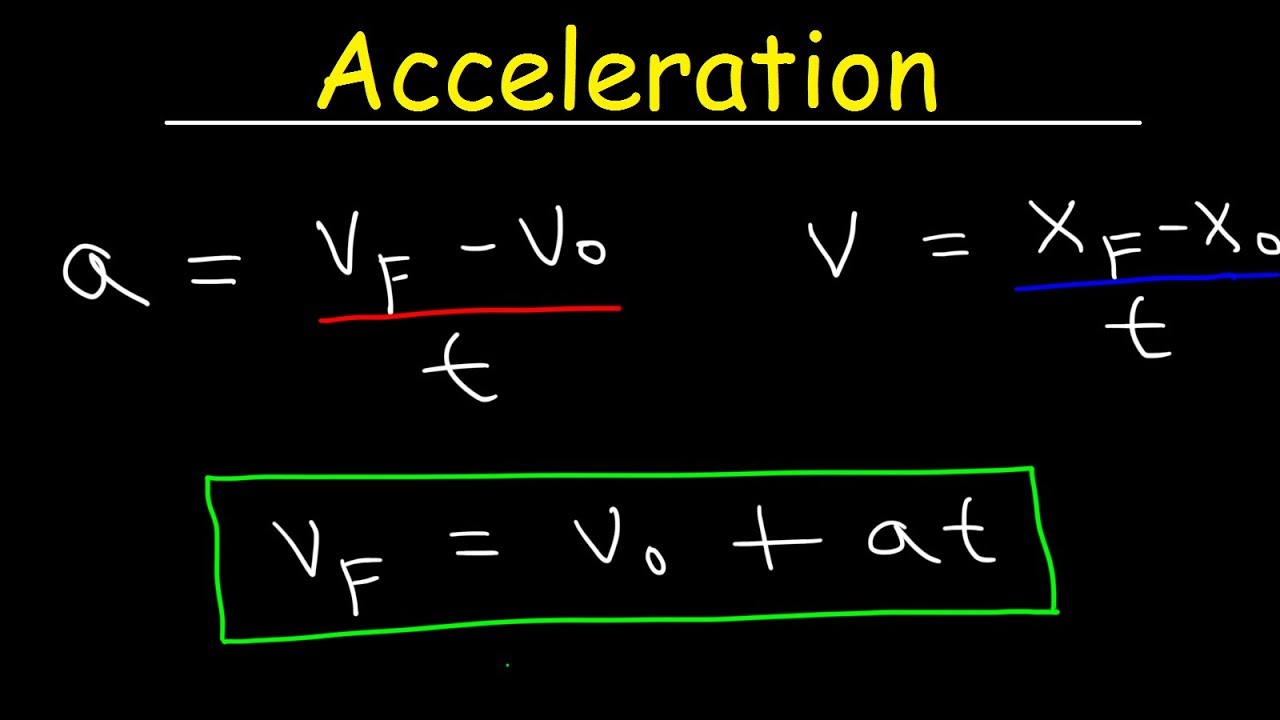
This allows a near-instant calculation of the solution. Internet browsers have a built-in JavaScript engine that can run this calculator inside the browser. The calculator on this page is written in the programming language JavaScript. If we are given time instead of distance, we would use equation 1. For example, if we are given the values for initial velocity (v 0), final velocity (v), and distance (Δx), we would use equation 2. We choose a kinematic equation based on what parameters we already know. After rearranging the terms in these three equations to solve for acceleration, they are given as: 1.) a = (v – v 0)⁄ t 2.) a = (v 2 – v 0 2)⁄ 2Δx 3.) a = 2(x – x 0 – v 0t)⁄ t 2 There are four kinematic equations, but only three of them can be used to solve for acceleration. These equations are known as the kinematic equations. Of course, we do not always know the change in velocity and elapsed time, so we must sometimes use other equations to solve for acceleration. In its simplest form, the equation for acceleration is given as: a = Δv⁄ t Where a is the acceleration of the object, Δv is the change in velocity, and t is the amount of time the change in velocity takes. It's not an easy endeavor, because such a leap required him to go up in a special balloon, and wear a custom-designed spacesuit that protected him from sudden shifts in temperature (after all, he was jumping from the edge of space).Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity for an object. Surprisingly, Eustace declined Google's help in the jump and funded the project himself. Eustace jumped from a heart-stopping height of 135,908 feet (41,425 m), thus setting a new record for a parachute jump. Alan Eustace, Google's VP of Knowledge, in 2014.
#Acceleration physics calculator free
One of the most extreme examples of an almost-scientifically-correct free fall is the jump of Dr. Nevertheless, this is as close to the actual experience as you can get on Earth 😉 In fact, a real free fall is only possible in a vacuum. Technically, such a jump doesn't fulfill all the requirements of a free fall - there is substantial air resistance involved. There are many ways to experience the thrill of a free fall - you could, for example, jump with a parachute or try bungee jumping! You might already have learned the free fall equation, but it's one thing to understand the theory and a completely different one to experience it. If you dropped the two items in a vacuum, they would both hit the ground at the same instant! Why does that happen? Again, because of air resistance. Or at least that's what science says! If you try to perform an experiment, you'll notice that, in reality, the brick falls to the ground first. If you drop a feather and a brick, they will hit the ground at the same time. It means that with each second, the falling body travels a substantially larger distance than before.Īnother interesting fact is that according to the free fall formula, the distance does not depend on the mass of the falling object. You can immediately see that the object distance traveled is proportional to the fall time squared. If the object is already traveling with an initial velocity, you have to take it into account, too: s = v₀t + (1/2)gt² If the initial displacement and velocity are both equal to zero, it boils down to: s = (1/2)gt² If you want to calculate the distance traveled by a falling object, you need to write down the equation of motion. If you want to consider it, head over to our free fall with air resistance calculator. In this free fall calculator, we neglect the influence of air resistance. According to Newton's first law, at that point, the falling body stops accelerating and moves at a constant speed. At some point, the two forces become equal in magnitude. The force of air resistance, however, increases with increasing free fall speed.

What is the terminal velocity? As you have seen above, the free fall acceleration is constant, which means that the gravitational force acting on an object is constant, too. In reality, though, a falling object's velocity is constrained by a value called the terminal velocity. Without the effect of air resistance, each object in free fall would keep accelerating by 9.80665 m/s (approximately equal to 32.17405 ft/s) every second. g is the free fall acceleration (expressed in m/s² or ft/s²).t stands for the fall time (measured in seconds) and.v₀ is the initial velocity (measured in m/s or ft/s).From the definition of velocity, we can find the velocity of a falling object is: v = v₀ + gt


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
